K-means clustering implementation in weka tool
Procedure:
Step1: Open the data file in Weka Explorer. It is presumed that the
required data fields have been discretized. In this example it is age
attribute.
Step2: Clicking on the associate tab will bring up the interface for
association rule algorithm.
Step3: We will use K-means algorithm. This is the default algorithm.
Step4:
Inorder to change the parameters for the run (example support, confidence etc)
we click on the text box immediately to the right of the choose button.
Scheme: weka.clusterers.SimpleKMeans -init 0
-max-candidates 100 -periodic-pruning 10000 -min-density 2.0 -t1 -1.25 -t2 -1.0
-N 3 -A "weka.core.EuclideanDistance -R first-last" -I 500 -num-slots
1 -S 10
Relation: labor-neg-data
Instances: 57
Attributes: 17
duration
wage-increase-first-year
wage-increase-second-year
wage-increase-third-year
cost-of-living-adjustment
working-hours
pension
standby-pay
shift-differential
education-allowance
statutory-holidays
vacation
longterm-disability-assistance
contribution-to-dental-plan
bereavement-assistance
contribution-to-health-plan
class
Test mode: evaluate on training data
=== Clustering model
(full training set) ===
kMeans
======
Number of iterations: 3
Within cluster sum of
squared errors: 119.5224194214812
Initial starting points
(random):
Cluster 0:
1,5.7,3.971739,3.913333,none,40,empl_contr,7.444444,4,no,11,generous,yes,full,yes,full,good
Cluster 1:
1,2,3.971739,3.913333,tc,40,ret_allw,4,0,no,11,generous,no,none,no,none,bad
Cluster 2:
2,2.5,3,3.913333,tcf,40,none,7.444444,4.870968,no,11,below_average,yes,half,yes,full,bad
Missing values globally
replaced with mean/mode
Final cluster
centroids:
Cluster#
Attribute Full Data 0 1 2
(57.0) (36.0) (5.0) (16.0)
========================================================================================
duration 2.1607
2.2267 1.4 2.25
wage-increase-first-year 3.8036 4.4695 3.2 2.4938
wage-increase-second-year 3.9717 4.4175 4.183 2.9027
wage-increase-third-year 3.9133 4.1093 3.9133 3.4725
cost-of-living-adjustment none none none none
working-hours 38.0392 37.4766 39.2078 38.94
pension empl_contr empl_contr none empl_contr
standby-pay 7.4444 7.9938 6.7556 6.4236
shift-differential 4.871 5.4776 3.1484 4.0444
education-allowance no no no no
statutory-holidays 11.0943 11.4801 10.6 10.3809
vacation below_average generous below_average below_average
longterm-disability-assistance yes yes no yes
contribution-to-dental-plan half half none half
bereavement-assistance yes yes no
yes
contribution-to-health-plan full full none full
class good good bad bad
Time taken to build
model (full training data) : 0.01 seconds
=== Model and
evaluation on training set ===
Clustered Instances
0 36 ( 63%)
1 5 (
9%)
2 16 ( 28%)
Scheme: weka.clusterers.SimpleKMeans -init 0
-max-candidates 100 -periodic-pruning 10000 -min-density 2.0 -t1 -1.25 -t2 -1.0
-N 2 -A "weka.core.EuclideanDistance -R first-last" -I 500 -num-slots
1 -S 10
Relation: labor-neg-data
Instances: 57
Attributes: 17
duration
wage-increase-first-year
wage-increase-second-year
wage-increase-third-year
cost-of-living-adjustment
working-hours
pension
standby-pay
shift-differential
education-allowance
statutory-holidays
vacation
longterm-disability-assistance
contribution-to-dental-plan
bereavement-assistance
class
Ignored:
contribution-to-health-plan
Test mode: Classes to clusters evaluation on training
data
=== Clustering model (full
training set) ===
kMeans
======
Number of iterations: 5
Within cluster sum of squared
errors: 122.05464734126849
Initial starting points (random):
Cluster 0: 1,5.7,3.971739,3.913333,none,40,empl_contr,7.444444,4,no,11,generous,yes,full,yes,good
Cluster 1:
1,2,3.971739,3.913333,tc,40,ret_allw,4,0,no,11,generous,no,none,no,bad
Missing values globally replaced
with mean/mode
Final cluster centroids:
Cluster#
Attribute Full Data 0 1
(57.0) (43.0) (14.0)
==========================================================================
duration 2.1607 2.213 2
wage-increase-first-year 3.8036 4.2024 2.5786
wage-increase-second-year 3.9717 4.221 3.2062
wage-increase-third-year 3.9133 4.0329 3.5462
cost-of-living-adjustment none none none
working-hours 38.0392 37.6557 39.2171
pension empl_contr empl_contr
none
standby-pay 7.4444 7.7778 6.4206
shift-differential 4.871 5.2018 3.8548
education-allowance no no no
statutory-holidays 11.0943 11.2878 10.5
vacation below_average
below_average below_average
longterm-disability-assistance yes yes yes
contribution-to-dental-plan half half none
bereavement-assistance yes yes yes
class good good bad
Time taken to build model (full
training data) : 0 seconds
=== Model and evaluation on
training set ===
Clustered Instances
0 43 ( 75%)
1 14 ( 25%)
Class attribute:
contribution-to-health-plan
Classes to Clusters:
0 1 <-- assigned to cluster
20 8 |
none
9 0 | half
14 6 |
full
Cluster 0 <-- none
Cluster 1 <-- full
Incorrectly clustered instances : 31.0
54.386 %
DATA MINING LABORATORY- IT6711
Hardware Requirements
RAM Memory -2 GB or more
Intel Pentium 4 or AMD Athlon 2 GHz (or faster)
1 GB (or more) available hard disk space
Software Requirements
SQL SERVER 2008,WEKA TOOL,JDK 1.8
RAM Memory -2 GB or more
Intel Pentium 4 or AMD Athlon 2 GHz (or faster)
1 GB (or more) available hard disk space
Software Requirements
SQL SERVER 2008,WEKA TOOL,JDK 1.8
EXPERIMENTS:
1. Creation of a Data Warehouse.
8. Support Vector Machines.
9. Applications of classification for web
mining.
10. Case Study on Text Mining
or any commercial application.
FP-Growth Algorithm implementation in weka tool
Procedure:
Step1: Open the data file in Weka Explorer. It is presumed that the
required data fields have been discretized. In this example it is age
attribute.
Step2: Clicking on the associate tab will bring up the interface for
association rule algorithm.
Step3: We will use FP-Growth algorithm. This is the default
algorithm.
Step4:
Inorder to change the parameters for the run (example support, confidence etc)
we click on the text box immediately to the right of the choose button.
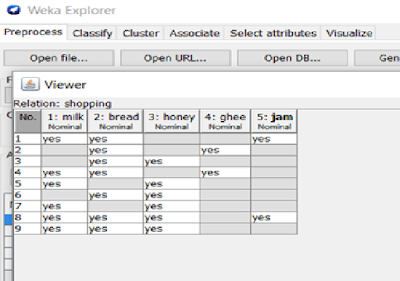
Data set:
Shopping.arff
@relation shopping
@attribute milk{yes,no}
@attribute bread{yes,no}
@attribute honey{yes,no}
@attribute ghee{yes,no}
@attribute jam{yes,no}
@data
yes,yes,no,no,yes
no,yes,no,yes,no
no,yes,yes,no,no
yes,yes,no,yes,no
yes,no,yes,no,no
no,yes,yes,no,no
yes,no,yes,no,no
yes,yes,yes,no,yes
yes,yes,yes,no,no
Apriori Algorithm implementation in weka tool
Procedure:
Step1: Open the data file in Weka Explorer. It is presumed that the
required data fields have been discretized. In this example it is age
attribute.
Step2: Clicking on the associate tab will bring up the interface for
association rule algorithm.
Step3: We will use apriori algorithm. This is the default algorithm.
Step4:
Inorder to change the parameters for the run (example support, confidence etc)
we click on the text box immediately to the right of the choose button.
Data set:
Shopping.arff
@relation shopping
@attribute milk{yes,no}
@attribute bread{yes,no}
@attribute honey{yes,no}
@attribute ghee{yes,no}
@attribute jam{yes,no}
@data
yes,yes,no,no,yes
no,yes,no,yes,no
no,yes,yes,no,no
yes,yes,no,yes,no
yes,no,yes,no,no
no,yes,yes,no,no
yes,no,yes,no,no
yes,yes,yes,no,yes
yes,yes,yes,no,no
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)